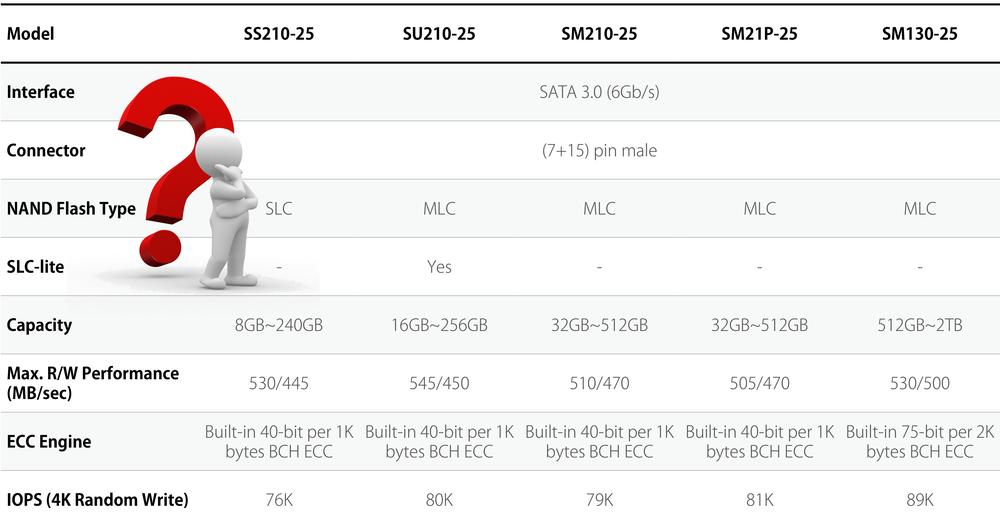
NAND Flash Memory Type
SLCSLC stands for single-level-cell. Memory cell is based on floating gate MOS transistor. Gate has either charge stored (0, programmed) or not (1, erased). SLC flash memory based SSDs are the most reliable, durable but also the most expensive SSDs. Apacer provides five years warranty (applies to the products shipped later than Jan. 1st, 2019) or the period ending on the date when the SSD has exceeded 60 000 erase count.
MLC and 3D TLC
MLC stands for multi-level-cell. Floating gate stores one of four amount of charge. TLC memory cell (triple-level-cell) stores charge in charge trap instead of floating gate. Charge trap stores one of the eight charge sizes. Apacer provides the same warranty for MLC and 3D TLC based products, two years warranty (one year for capacity 4GB or lower) or the period ending on the date when the SSD has exceeded 3 000 erase count for the both technologies.
SLC-Lite
SLC-Lite technology uses MLC flash chips, but firmware either stores charge to floating gate or not - the same procedure as for SLC. Such strategy significantly increases the erase count and allows Apacer to provide three years warranty or the period ending on the date when the SSD has exceeded 20 000 erase count. Erase count is indicated by Apacer SMART software as parameter Avg.erase Count.
Capacity
Apacer uses convention where 1GB=1000MB. Operating systems uses convention where 1GB=1024MB. For example, 64GB MLC mSATA from SM210-300 series datasheet mentions 64 023 257 088 total Bytes and capacity 64GB. Operating system will show capacity 64 023 257 088/1024^3=59,63GB. Usable capacity will be lower because small portion of the capacity is required by file system. NTFS consumes 66,31MiB, EXT4 uses 1,24GiB and XFS only 29,92MiB. SLC flash based SSDs are available up to 240GB capacity, SLC-Lite SSDs offer up to 256GB capacity and MLC flash SSDs up to 2TB.
Speed
This parameter defines how many data can be written to SSD. Value is expressed in TBW (Tera Bytes Written), where 1TB=1 000GB or in DWPD (Drive Writes per Day) indicating how many times a day the user can overwrite the entire capacity of SSD during the warranty period.
Estimation complies with JEDEC JESD-219, enterprise endurance workload of random data with payload size distribution. Real endurance always depends on structure of data written to or read from SSD. It is highly recommended to use Apacer SSDWidget, which provides information about health status of SSD and SMART attributes values. For more information about SSDWidget, please see user manual.
Endurance vs. Erase Count
Simple consideration leads to result that Endurance= Avg.erase Count*Capacity. Let’s verify it for 64GB SM210-25 MLC SSD. Endurance=3 000*64GB=192TB. But datasheet mentions 142TB. This discrepancy is caused by the fact that the actual amount of data physically written to the flash is higher than the amount intended to be written by operating system due to Write amplification (WA).
WA= Data written to flash memory/Data written by operating system.
For our 64GB SSD, if host writes 142TB of data Avg.erase Count = 3 000, then WA=192/142=1.352.
For real workload:
Data written to flash memory = Avg.erase Count*Capacity
Data written by host = Total Sectors of Write * Bytes per sector
Avg.erase Count: SMART parameter 164
Capacity: 64GB (from datasheet)
Total Sectors of Write: SMART parameter 241
Bytes per sector=512 (from datasheet)
SATA Revision
Serial ATA specification is managed by Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO). Apacer SSDs are compliant with revision 3.2 or 3.1 (6 Gb/s). SSDs are backward compatible with SATA 2.x (3Gb/s) and SATA 1.x (1.5Gb/s) interface.
SMART
SMART is an abbreviation for Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology. Firmware monitors the important SSD parameters for taking proactive measures to prevent its failure. Explanation of the most important attributes is described below.
166, Total Later Bad Block Count
Normally the later bad block number will only increase significantly when the erase count is close or above maximal erase count, 3000 (MLC, TLC), 20 000 (SLC-Lite) or 60 000 (SLC). If the erase count is lower than maximal and the number of new defective blocks increases, this is an abnormal situation. Backup data immediately.
166, Total Later Bad Block Count, 192, Unexpected Power Loss Count
If Total Later Bad Block Count increases when Unexpected Power Loss Count increases, you should take precaution to avoid power loss occurrence.
231, Lifetime Left
Value in percent, 100% means a new SSD, 5% - warning, you should replace SSD. For SSD which doesn’t provide this information, attribute 164, Avg. Erase Count can be used to calculate lifetime left.
Lifetime Left = (1 - Avg. Erase Count/Max. erase count) x 100, Max. erase count =3000 (MLC, 3D TLC), 20 000 (SLC-Lite) or 60 000 (SLC).
167, SSD Protect Mode
• 0: R/W – normal status
• 3: Read Only
• 7: Occurs when free blocks are insufficient or encountering excessive later bad blocks
SSD protects written data by setting to read-only mode to avoid data corruption if Avg. Erase Count exceeds allowed PE cycles or Unusual Read Only event occurs.
171, Program Fail Count, 172, Erase Fail Count
These parameters should always be 0, if not, you should replace SSD.
168, SATA PHY Error Count
Indicates problems with communication through SATA interface.
194, Temperature
Temperature has to be lower than max. allowed temperature. Sensor measures the temperature in defined point on the SSD PCB so that the measured value is close to ambient temperature.
Power Failure Management
SSD contains power supply voltage supervisor. If voltage drops below predefined threshold, SSD controller will run urgent metadata write to flash for later mapping table rebuilding. This operation requires about several milliseconds to get it done. Though unlikely to happen in most cases, the SSDS with DRAM write cache might be potentially affected if a sudden power loss takes place before the cached data is flushed into flash.
To increase immunity against data loss during power failure, Apacer uses CorePower technology. SSD contains bank of tantalum capacitors that supply energy for time required for flushing cached data in DRAM and essential metadata into flash.
Device Sleep
SSD in DevSleep mode consumes less than 5mW. DevSleep uses a new signal (DEVSLP). When the host asserts the DEVSLP signal, the device enters the DevSleep mode for as long as the host asserts the DEVSLP signal. When the host negates the DEVSLP signal, the device returns from the DevSleep state within 20ms. For 2.5” SSD, DEVSLP signal is connected to P3 pin on SATA power connector. If P3=3.3V SSD enters to DevSleep mode. mSATA SSDs use pin 44, M.2 SSDs use pin 38.
ATA Secure Erase
Defined in ATA specifications, secure erase allows storage drives to wipe all data stored by user. The erase process runs on the firmware level. The most convenient way to do it is using the Apacer SSDWidget.
TRIM
The command enables the operating system to inform SSD controller which blocks contain invalid data, mostly because operating system deleted files. TRIM support is important for maintaining write speed of SSD. All modern SSDs and operating systems support TRIM. You can find more information on how TRIM works in Wikipedia.
For further information about APACER products, please do not hesitate to contact us at apacer@soselectronic.com
Do you like our articles? Do not miss any of them! You do not have to worry about anything, we will arrange delivery to you.