We tried it out.
We did it and can help you with that too.
First of all, you should have information about the NarrowBand operator - the Internet of Things in your country. If you want to connect, you need an accessible network in your neighbourhood. Before you begin, check the coverage level with your operator.
What you need to connect:
- device with which you send the data. We offer the tested Quectel development kit and the BC 95 module
- SIM card of your operator running the NB network in your country
- server to which you will send the data (NB Network operator usually offers access to the server along with the card).
Ask your operator about the purchase of the NB-IoT SIM cards and the data server provision. We can offer you the NB-IoT Start-up package (development kit and module) from our warehouse.
Connection process
Enable scrambling and settings:
AT+CFUN=1 // enable scrambling functionAT+NCONFIG=CR_0354_0338_SCRAMBLING,TRUE
AT+NCONFIG=CR_0859_SI_AVOID,TRUE // disable auto connect and multitone
AT+NCONFIG=AUTOCONNECT,FALSE
AT+NCONFIG=MULTITONE,FALSE (BC95-G/BC68 only) // Reboot the module
AT+NRB
Set Band, APN & URCs:
//set band 8=900 MHz, 20=800 MHz from operator//
AT+NBAND=20 //Set APN for PDP context, ("") from operator
AT+CGDCONT=1,"IP","u.iot.mt.gr.hu" //Enable network registration, connection & PSM URCs
AT+CEREG=2
AT+CSCON=1
AT+NPSMR=1
Manual operator selection:
1. Turn on the modem:
AT+CFUN=1 // set MCC MNC values, ex: 123456 pre MCC=123 MNC=56
2. Log in ( 30 seconds ):
AT+COPS=1,2,"21630"
3. Registration:
/ wait 30 sec for NW registration of URC 1=home alebo 5=roaming /
+CEREG:1,xxxx,yyyyy,z
+CEREG:5,xxxx,yyyyy,z
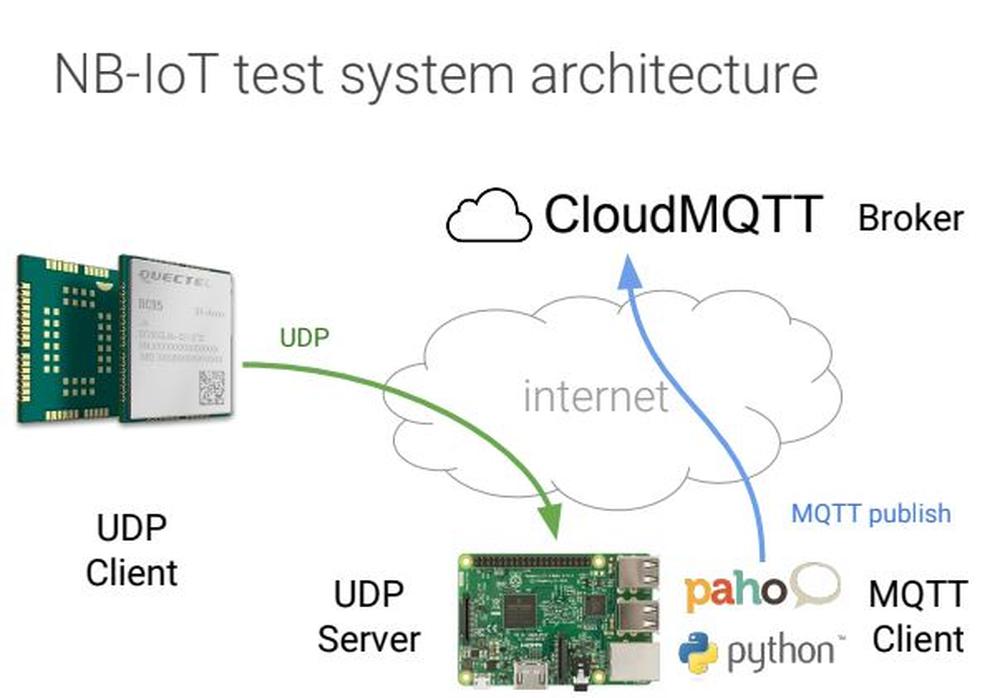
Send/Receive UDP data:
1. create an UDP socket
AT+NSOCR= DGRAM,17,16666,1
0
2. send UDP message
AT+NSOST=0,83.58.228.64,16666,12,48656C6C6F20576F726C6421
0,12
+NSONMI:0,12
3. received UDP message
AT+NSORF=0,12
0,83.58.228.64,16666,12,48656C6C6F20576F726C6421,0
4. close socket
AT+NSOCL=0

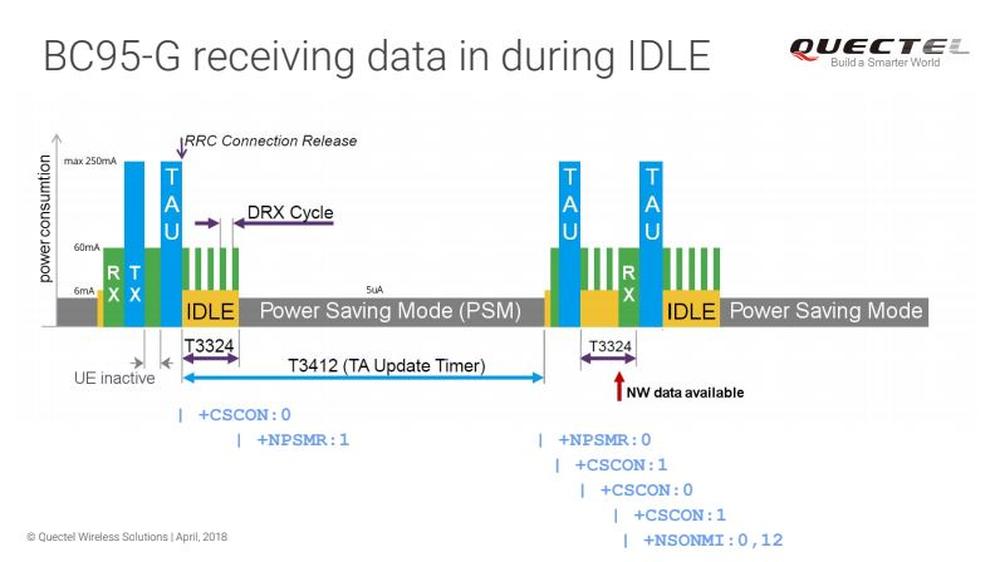
BC95G receiving data in IDLE:
+CSCON: 0 // enter IDLE mode, release connection
+NPSMR: 1 // enter PSM mode
+NPSMR: 0 // wakeup from PSM mode
+CSCON: 1 // connect
+CSCON: 0 // enter IDLE mode
// message received during paging while IDLE
+CSCON: 1 // exit IDLE mode, connect
+NSONMI: 0,12 // UDP message received
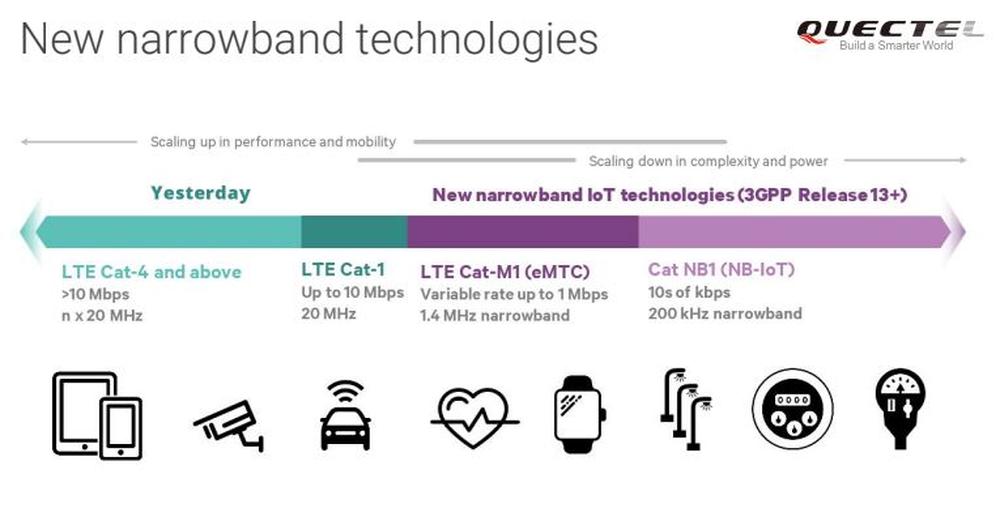
What is NB-IoT?
NB-IoT is a special narrowband network. It is mainly designed to transfer smaller volumes of data at higher speeds. And it is often associated with IIoT - Industry Internet of Things - The Industrial Internet of Things.
NB-IoT significantly improves network efficiency. It increases the capacity to support a huge number of new connections. It can connect up to 50,000 devices per one NB-IoT network.
We can see the unique benefits in:
- coverage, even in hardly accessible places (underground, under water, etc.)
- the ability to penetrate; so-called signal penetration in buildings
- low energy consumption (battery life even 10 years, depending on the volume of transferred data)
- data transfer security and reliability compared to mobile networks.
Extensive use is found in industry, agriculture, healthcare, logistics, "smart cities and buildings". It is expected to make work easier for technicians, salesmen, and carriers when operating the machines, sensing technological values, and with remote monitoring. They can see and monitor their means of production/goods. They can immediately find out what their status is and what’s happening to them. We are talking about two-way communication, i.e. terminal devices can be remotely controlled and set up via simple application or web.
The NB-IoT network fully covers the Czech Republic and Germany. Slovakia, Austria and Poland currently have a partial coverage of the territory. Hungary has a very good signal around the capital, Budapest. The remaining European countries that plan to cover the entire territory by 2020 are Spain, Ireland, Italy, and the Netherlands.
Do you like our articles? Do not miss any of them! You do not have to worry about anything, we will arrange delivery to you.